- Database Environment.
- Information Technology (IT) Department.
- Database Administrator.
- Database Administration Categories (DBA).
- Responsibilities of a Database Administrator.
- Daily tasks of a database administrator.
- Skills require to become a database administrator.
1.0 Database Environment.
A database environment is a collective system of components that comprise and regulates the group of data, management, and use of data, which consist of software, hardware, people, techniques of handling database, and the data also.
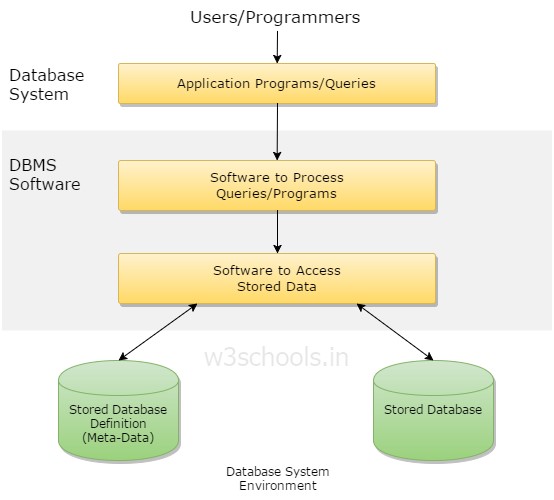
Here, the hardware in a database environment means the computers and computer peripherals that are being used to manage a database, and the software means the whole thing right from the operating system (OS) to the application programs that include database management software like M.S. Access or SQL Server. Again, the people in a database environment include those people who administrate and use the system. The techniques are the rules, concepts, and instructions given to both the people and the software along with the data with the group of facts and information positioned within the database environment.
1.1 Information Technology (IT) Department.
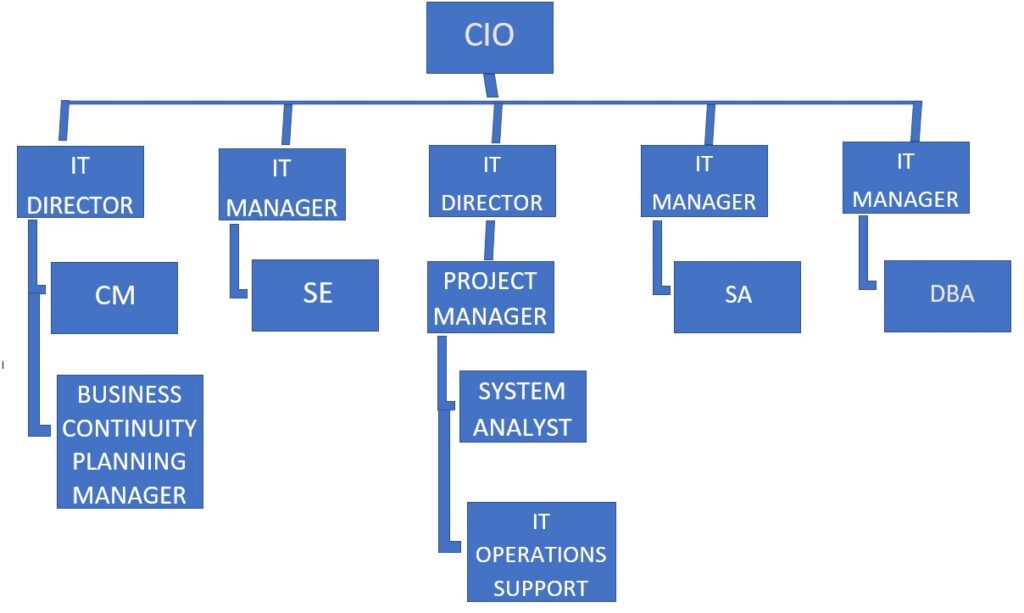
An IT organization (information technology organization) is the department within a company that is charged with establishing, monitoring, and maintaining information technology systems and services.
In a large organization, the IT organization may also be charged with strategic planning to ensure that all IT initiatives support business goals. IT organizational structures vary and can be centralized or decentralized depending upon the needs of the company. In a large enterprise, the IT organization is typically managed by a Chief Information Officer (CIO). Smaller IT organizations might report up to an IT director or operations manager.
1.2 Database Administrator.
A database administrator (DBA) is a specialized computer systems administrator who maintains a successful database environment by directing or performing all related activities to keep the data secure. The top responsibility of a DBA professional is to maintain data integrity. This means the DBA will ensure that data is secure from unauthorized access but is available to users.
A database administrator will often have a working knowledge and experience with a wide range of database management products such as Oracle-based software, SAP and SQL, in addition to having obtained a degree in Computer Science and practical field experience and additional, related IT certifications.
1.3 Database Administrator Categories (DBA).
There exist several Categories of DBAs, some of which and their roles are:
1.3.1 Administrative DBA.
Work on maintaining the server and keeping it running. Concerned with backups, security, patches, High Availability, Disaster recovery migration, upgrading and everything that concern the actual server software.
1.3.2 Development DBA.
Concerned with building stored procedures, building queries, writing codes that meet business needs. This is the equivalent of a programmer.
1.3.3 Database Architect.
Design schemas, build tables, Primary keys, Foreign keys. They work to build a structure that meets the business in general. The design is then used by developers and development DBAs to implement the actual application.
1.3.4 Data Warehouse DBA.
Responsible for merging data from multiple sources into a data warehouse. May have to design warehouse, but cleans, standardize, and scrubs data before loading. In SQL server this DBA will use Data Transformation Service (DTS) oftentimes.
1.4 Responsibilities of a Database Administrator.
The following are some key responsibilities of a database administrator.
- Installation, configuration and upgrading of Microsoft SQL Server and related products.
- Implement and maintain database security (create and maintain users and roles, assign privileges, masking, Transparent Data Encryption, Always Encrypted)
- Implement Disaster Recovery (establish and maintain sound backup and recovery policies and procedures)
- Ensure high availability (Always On availability groups, clustering)
- Database tuning and performance monitoring.
- Take care of the database design and implementation.
1.5 Daily tasks of a database administrator.
The following are some of the daily activities of a database administrator.
- Attend meetings with other team members for the implementation of new applications.
- Review emails and ticketing system.
- Answer users request.
- Review monitoring tools for potential issues.
- Work on projects.
1.6 Skills require to become a database administrator.
Below are list of skills required to become database administrators:
- Knowledge of database queries
- Knowledge of database theory
- Knowledge of database design
- Knowledge about the RDBMS itself, e.g. Microsoft SQL Server or MySQL
- Knowledge of structured query language (SQL), e.g. SQL/PSM or Transact-SQL
- General understanding of distributed computing architectures, e.g. Client–server model
- General understanding of operating system, e.g. Windows or Linux
- General understanding of storage technologies and networking
- General understanding of routine maintenance, recovery, and handling failover of a database.


Hi, this is a comment.
To get started with moderating, editing, and deleting comments, please visit the Comments screen in the dashboard.
Commenter avatars come from Gravatar.
[url=https://clonidine.site/]clonidine 0 2mg[/url]
[url=http://buycafergot.life/]cafergot medication generic[/url]
[url=http://agabapentin.com/]generic neurontin pill[/url]
[url=https://propecial.monster/]propecia how to get[/url]
[url=http://vermoxtabs.com/]vermox 500mg tablet[/url]
[url=http://ampicillin.fun/]ampicillin 250 mg caps[/url]
[url=https://bupropiontab.online/]zyban cost without insurance[/url]
[url=http://azithromycingn.online/]where can i buy azithromycin 500mg[/url]
[url=https://buspar.store/]buspar 60 mg daily[/url]
[url=https://buykamagra.monster/]kamagra oral jelly 100mg[/url]
[url=http://acyclovirztab.online/]can i buy acyclovir over the counter uk[/url] [url=http://lisinoprilb.online/]lisinopril generic[/url] [url=http://amoxicillina.org/]order augmentin over the counter[/url] [url=http://tetracycline.icu/]buy tetracycline tablets[/url] [url=http://accutane.life/]price of accutane in india[/url]
[url=https://gabapentintabs.shop/]neurontin 330 mg[/url]
[url=http://accutane.fun/]best accutane brand[/url] [url=http://buykamagra.monster/]kamagra oral jelly for sale in south africa[/url]
[url=https://allopurinol.email/]allopurinol online[/url]
[url=http://gabapentintabs.shop/]buy gabapentin online usa[/url]
[url=http://modafinil24.net/]order provigil online[/url]
[url=https://gabapentintabs.shop/]gabapentin gel[/url]
[url=http://tretinointabs.com/]tretinoin .1 cream online[/url] [url=http://buyamoxicillin.life/]where can you get amoxicillin[/url] [url=http://tetracycline.icu/]buy tetracycline 500mg online[/url] [url=http://acyclovirztab.online/]cost of zovirax tablets[/url]
[url=http://iveromectina.net/]ivermectin otc[/url]
[url=https://bupropiontab.online/]bupropion brand name australia[/url]
[url=http://azithromycingn.online/]azithromycin otc us[/url] [url=http://lasixm.monster/]lasix without prescription usa[/url] [url=http://tretinointabs.com/]tretinoin 1 cream for sale[/url] [url=http://buykamagra.monster/]kamagra oral jelly distributor[/url] [url=http://cipros.shop/]ciprofloxacin 250 mg tablet[/url] [url=http://buymusclerelaxants.com/]4mg zanaflex[/url] [url=http://augmentin.run/]amoxicillin 500 mg without a prescription[/url]
[url=http://cipro.life/]cipro no prescription canadian pharmacy[/url]
[url=https://acyclovirztab.online/]zovirax singapore price[/url]
[url=https://fluoxetine.click/]fluoxetine drug[/url] [url=https://colchicine.run/]how much is the price of colchicine[/url] [url=https://cipro.life/]buy ciprofloxacin 500mg online uk[/url] [url=https://modafinilb.quest/]can you buy modafinil in mexico[/url] [url=https://cleocintabs.online/]clindamycin 300mg capsules[/url] [url=https://valtrexd.online/]valtrex 500[/url] [url=https://tretinoinretina.shop/]tretinoin cream 15g[/url]
[url=https://acyclovirztab.online/]zovirax 800[/url]
[url=http://lasix.works/]lasix 20 mg price[/url]
[url=http://levitratabs.monster/]cost of vardenafil[/url]
[url=http://albuteroltab.online/]albuterol[/url]
[url=http://finasteridemed.com/]propecia over the counter canada[/url] [url=http://synthroidlevothyroxine.shop/]synthroid 125 mcg cost[/url] [url=http://onlinedrugstore.click/]us pharmacy no prescription[/url]
[url=http://onlinedrugstore.click/]happy family pharmacy discount code[/url]
[url=http://finasteridemed.com/]finasteride 5mg nz[/url]
[url=http://synthroidm.online/]average cost of synthroid[/url]
[url=http://albuteroltab.online/]buy cheap ventolin online[/url]
[url=http://azithromycinc.online/]zithromax cream[/url] [url=http://diclofenactab.quest/]cheap voltaren gel[/url] [url=http://modafiniltab.net/]modafinil 2014[/url] [url=http://accutanex.online/]accutane tablets[/url] [url=http://onlinedrugstore.click/]pharmacy canadian superstore[/url] [url=http://paxiltab.online/]paroxetine in india[/url] [url=http://buylisinoprilwithoutprescription.com/]prescription medicine lisinopril[/url] [url=http://aurogra.fun/]aurogra 200[/url]
[url=https://azithromycinc.online/]azithromycin 600 mg india[/url]
[url=https://buyretinoa.monster/]retino 0.25 cream[/url]
[url=https://tretinointabs.online/]where can i buy retin a 0.05[/url]
[url=http://seroquelquetiapine.shop/]seroquel xr[/url]
[url=https://modafiniltab.net/]provigil 200 mg price[/url]
[url=http://prozactabs.online/]canadian pharmacy fluoxetine[/url]
[url=https://deltasoneprednisone.shop/]over the counter prednisone pills[/url]
[url=http://acyclovira.com/]acyclovir best price[/url]
[url=http://lyricatabs.quest/]lyrica generic medication[/url]
[url=https://pharmacies.quest/]pharmacy rx[/url]
[url=https://trazodonedesyrel.shop/]trazodone pill[/url]
[url=https://clonidine.run/]clonidine catapres[/url]
[url=https://buyadvair.life/]canadian pharmacy advair diskus[/url]
[url=https://pregabalinlyrica.shop/]lyrica capsules 25 mg[/url]
[url=https://clonidine.run/]clonidine purchase[/url]
[url=http://noroxina.shop/]generic noroxin[/url]
[url=https://buyadvair.life/]advair buy online[/url]
[url=http://deltasonetab.online/]order prednisone online[/url]
[url=https://tamoxifen.sbs/]tamoxifen uk online[/url]
[url=https://orderviagratabs.com/]sildenafil no rx[/url]
[url=https://cephalexinv.com/]keflex price australia[/url]
[url=https://advairtab.online/]advair cream[/url]
[url=https://orderviagratabs.com/]us online pharmacy viagra[/url]
[url=https://plavixtabs.quest/]medication plavix 75mg[/url] [url=https://pregabalinlyrica.shop/]lyrica 75 mg generic[/url] [url=https://pharmacies.quest/]canadian pharmacy no rx needed[/url] [url=https://lasixtabs.shop/]lasix 40mg to buy[/url] [url=https://fluoxetine247.com/]generic prozac 40 mg tablet[/url] [url=https://noroxintabs.quest/]noroxin medication[/url] [url=https://hydroxychloroquinetab.shop/]where to buy plaquenil[/url]
[url=http://valtrexd.quest/]valtrex.com[/url]
[url=http://medrol.cfd/]medrol pill[/url]
[url=https://buyamitriptyline.life/]amitriptyline 150 mg tablet[/url]
[url=https://buyamitriptyline.life/]amitriptyline prescription[/url]
[url=http://levofloxacin.cfd/]purchase levaquin[/url]
[url=http://paxil.run/]paroxetine cost without insurance[/url]
[url=https://cymbaltatabs.online/]40 mg cymbalta[/url]
[url=https://erectafil.life/]buy erectafil 20[/url]
[url=https://erectafil.life/]erectafil 5[/url]
[url=http://diclofenactabs.online/]voltaren tablets over the counter[/url]
[url=http://medrol.cfd/]medrol 4mg tablet price[/url]
[url=https://lexaproescitalopram.online/]lexapro 10 mg tablet price[/url]
[url=https://medrol.cfd/]medrol 4 mg tab[/url]
[url=https://seroqueltab.quest/]seroquel coupon[/url]
[url=http://azithromycinz.shop/]where to buy azithromycin 500mg[/url]
[url=http://celexatab.monster/]citalopram 20mg pill[/url]
[url=http://metformind.quest/]metformin singapore[/url]
[url=http://avodart.life/]generic avodart 0.5 mg[/url]
[url=http://singulaira.online/]buy singulair online canada[/url]
[url=http://plavix.life/]clopidogrel pill[/url]
[url=https://sildenafilcitrategenericviagra.com/]buy viagra online without prescription[/url]
[url=http://dapoxetinetabs.online/]dapoxetine for sale in usa[/url]
[url=http://viagra2023.com/]pfizer viagra online pharmacy[/url]
[url=https://sildenafilcitrategenericviagra.com/]buy viagra online in canada[/url]
[url=https://metforminv.quest/]metformin 1000[/url]
[url=https://cozaar.life/]cost of cozaar 100 mg[/url]
[url=http://celexatab.monster/]40 mg celexa[/url]
[url=https://abilifytabs.monster/]canadian cost abilify[/url]
[url=http://fluconazole.click/]diflucan over counter[/url]
[url=http://cleocintabs.shop/]cleocin 600 mg tablet[/url]
[url=https://priligy.icu/]cheap priligy[/url]
[url=https://effexorvenlafaxine.online/]75 mg effexor[/url]
[url=https://buypriligy.life/]priligy tablets canada[/url]
[url=http://buylexapro.life/]lexapro for sale uk[/url]
[url=http://levothyroxine.cfd/]brand name synthroid price[/url]
[url=https://buystromectol.life/]cheap stromectol[/url]
[url=http://suhagram.monster/]suhagra 50 mg price[/url]
[url=https://indocin.sbs/]indocin 25mg cap[/url]
[url=http://buyyasmin.life/]yasmin nouri[/url]
[url=http://tetracyclinetab.online/]tetracycline over the counter uk[/url]
[url=https://tamoxifena.monster/]buy nolvadex online pharmacy[/url]
[url=http://fluconazole.sbs/]diflucan tablets for sale[/url]
[url=https://buylexapro.life/]where can i get lexapro brand medication[/url]
[url=https://viagrawithoutprescription.com/]viagra singapore price[/url]
[url=http://diflucantabs.online/]otc diflucan pills[/url]
[url=https://metformind.online/]glucophage 100 mg[/url]
[url=https://xmodafinil.online/]modafinil medication[/url] [url=https://tretinoincream01.com/]retin-a generic[/url]
[url=http://levothyroxine.cfd/]buy generic synthroid[/url]
[url=https://buytamoxifen.life/]tamoxifen price india[/url]
[url=http://xmodafinil.online/]modafinil prescription usa[/url] [url=http://albenza.life/]albendazole how to[/url] [url=http://suhagram.monster/]suhagra 50 price[/url]
[url=https://atarax.life/]atarax uk[/url]
[url=http://budesonide.icu/]budesonide tablet brand name[/url]
[url=https://albuteroltabs.com/]albuterol inhaler price[/url]
[url=https://phenergan.life/]phenergan 12.5[/url]